A common challenge for many businesses is efficiently managing user permissions as new solutions are deployed and adopted. How do you ensure that the right people have the right permissions to access the data they need for their jobs? Missteps on provisioning permissions can lead to unauthorized access to data, creating major headaches for IT and security teams.
One way around this challenge is to start with solid user and permission management practices that help you assign access to your users, such as role-based access control (RBAC). RBAC is a security approach that authorizes and restricts users' access based on their roles within an organization. While RBAC is an effective way to manage user access control at scale, you can add extra layers of protection to ensure that the right roles are being assigned. A good example of this would be using hierarchies to propagate the inheritance of permissions.
Let's take a look at how you can use runZero organizations for data segmentation and hierarchies to streamline user permission management.
The role of organizations #
Organizations are a powerful feature that allow you to create separate entities for your assets and control what users can do with the organizational data. In runZero, you can use organizations to group and manage asset data, Explorers, tasks, sites, and scan configurations. The flexibility of organizations allows you to segment your data by company, department, customers, or however you like. For example, you might want to set up different organizations for each environment you have – such as development and production – because you want to segment the data. Or if you're a service provider, you may have an organization for each one of your customers.
In some cases, your business may want to set up multiple organizations to manage asset data as well as streamline permissions management. Imagine having to review and assign organizational access for each user. That's time-consuming and prone to user error. So how can you ensure consistent provisioning of user permissions throughout your organizations?
Introducing organizational hierarchies #
runZero 3.6 introduces organizational hierarchies, which enables you to create parent-child relationships between organizations. This approach is based on a top-down permissions distribution model, where the child organizations inherit the permissions configured within the parent organization.
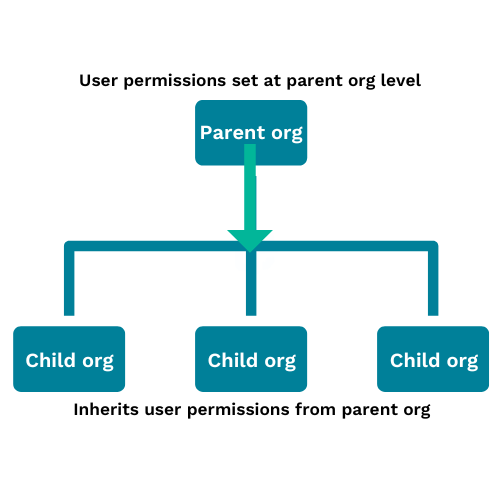
The parent organization sets the minimum permission level a user has to that organization and any children. Child organizations with lower permissions than the parent organization will inherit the effective higher permission. For example, if the parent organization has a user's permissions set to annotator, then the child organizations can be upgraded to user or administrator, but downgraded permissions won't have any effect.
Imagine you have a parent organization called Mom Org that has a child organization called Baby Org. Within Mom Org, a user named Chris has been assigned an administrator role. As a result, Chris can access the Baby Org organization as an administrator.
Let's take a look at how you can set up organizational hierarchies in runZero.
How to set up organizational hierarchies in runZero #
To set up an organizational hierarchy, you can either create a new organization or modify an existing one. You can always edit your organizations and assign a new parent (or no parent at all).
Here's how you can assign a parent organization:
- Create a new organization or edit an existing organization.
- Make sure to provide a name and description for the organization. This information captures context about the organization and the type of data it contains.
- Make sure to set any expiration dates for stale assets, offline assets, and scan data. This determines how long these data types are stored by runZero.
- Under parent settings:
- If you want to add the organization under a parent organization, choose an organization to assign as the parent. You can choose a child organization to be a parent as well – runZero supports up to three levels of nesting.
- If you don't want to assign a parent to the organization, choose
None. You can add child organizations later, if needed.
- Save your organization.
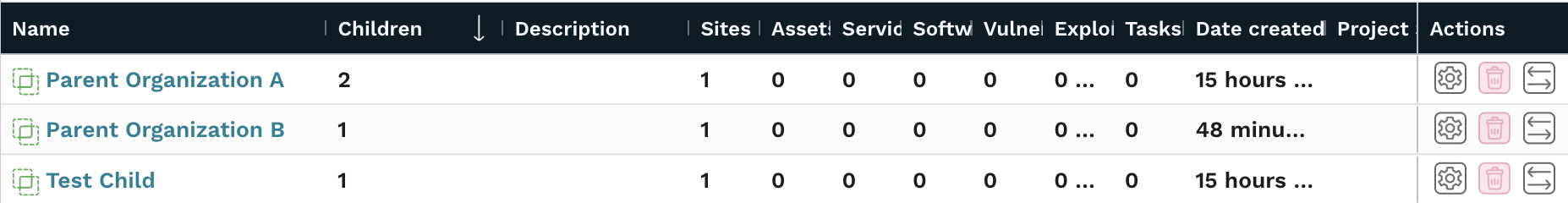
After you save your changes, the new hierarchical permissions will take effect. From the Organizations page, you can see how many children each organization has.
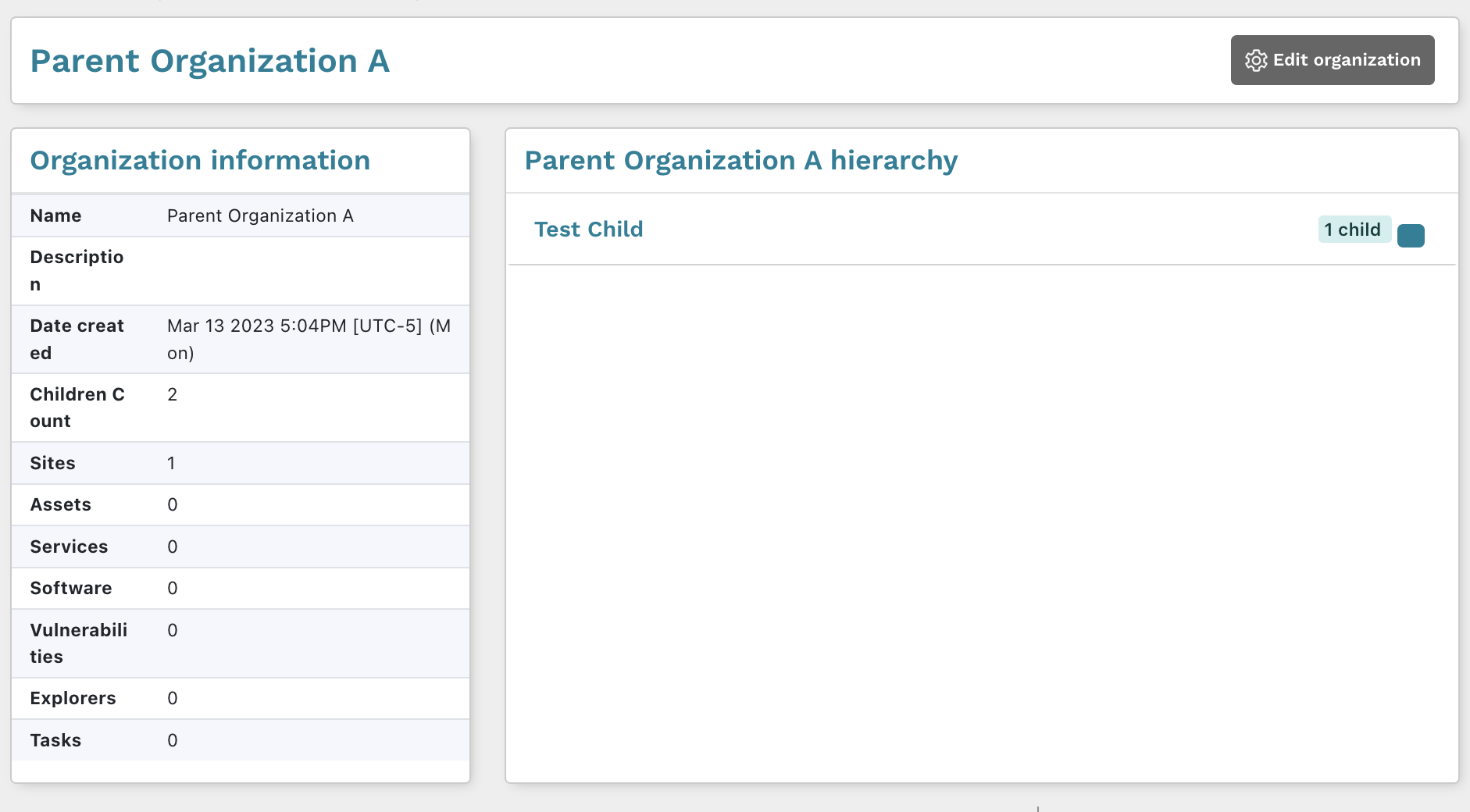
Additionally, you can view the details page for a specific organization to see the parent hierarchy.
How to view user permissions #
To see what a user's permissions look like, you can view a user's details to see their role for each organization.
- Go to your Users page and click the name of the user whose permissions you want to view.
- The user details page shows a table that contains all of the organizations that the user has access to and the role that they are assigned.
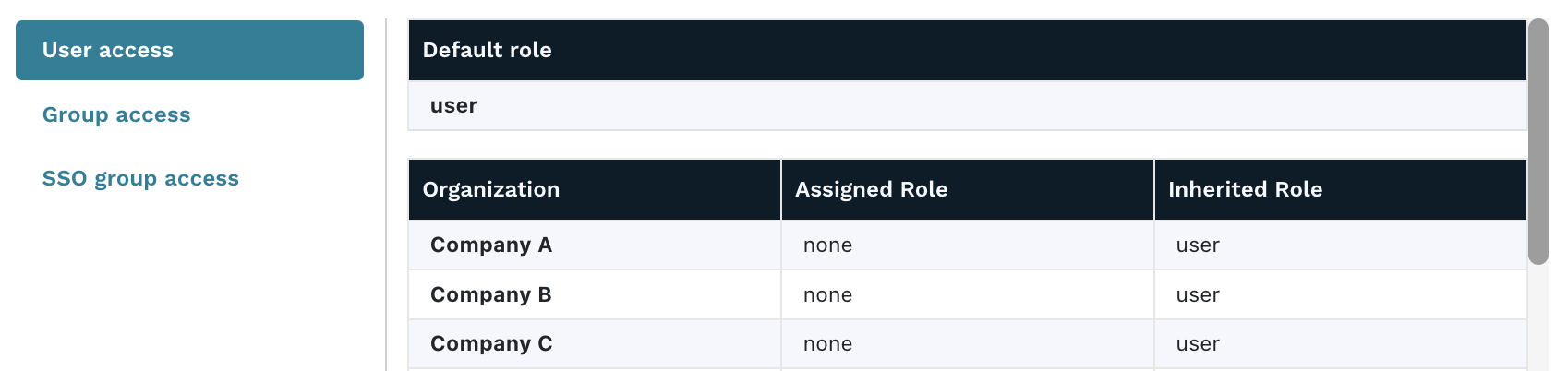
If the role is listed in the Assigned role column, then it was explicitly configured for the user. If the role is listed in the Inherited role column, then the permissions were set by the default role or parent organization. The higher level of the two columns will be the effective access that the user has to that organization.
Simplify the complexities of user access management with organizational hierarchies #
As your business continues to grow and scale, so does the need for control over complexity. To protect and secure your data, you need to have the right systems and measures in place for effective user access management. Once you have solid RBAC practices in place, you can add extra layers of protection, such as organizational hierarchies, to ensure that the right roles are being propagated to users.
Ready to get a stronger handle on user and permission management in runZero? Try out organizational hierarchies today.