Latest vulnerability: CVE-2024-43491 #
On September 10, 2024, Microsoft disclosed a vulnerability affecting Windows 10, version 1507. The vulnerability was discovered by Microsoft's Windows product team. The vulnerability was exposed in the Servicing Stack after rolling back fixes for vulnerabilities within Optional Components earlier this year.
This vulnerability has been designated CVE-2024-43491 and has been given a CVSS score of 9.8 (critical).
What is the impact? #
Although the details of the vulnerability aren't publicly available, an attacker capable of exploiting a vulnerable system could execute arbitrary code, potentially leading to system compromise.
Are updates or workarounds available? #
Microsoft has released updates that address this vulnerability and recommends all users update as quickly as possible. Systems configured to auto-update should already have the servicing stack and security updates applied.
How to find potentially vulnerable systems with runZero #
From the Asset Inventory you can use the following query to locate potentially affected Windows 10 systems:
os:"Windows 10 Enterprise 2015" OR os:"Windows 10 IoT Enterprise 2015" OR (os:"Windows 10" AND os_version:"1507")70 vulnerabilities (May 2022) #
In May 2022 Microsoft released security updates for over 70 vulnerabilities, including 3 zero-days and 7 critical vulnerabilities that affected a wide-range of their products and services. The list of patches covered an actively exploited zero-day vulnerability in the Windows Local Security Authority (LSA), as well as vulnerabilities in Kerberos, NFS, and LDAP protocols.
What was the impact of these vulnerabilities? #
CVE-2022-26931 was a critical Kerberos vulnerability that provided an attacker with privilege elevation if successfully exploited.
CVE-2022-26937 was a critical NFS vulnerability included in the list of fixes. This vulnerability could allow an unauthenticated attacker to execute arbitrary code if successfully exploited over the network. Microsoft recommended disabling NFSV2 and NFSV3 as a means of exploit mitigation using the following PowerShell command. NFSv4.1, is not vulnerable:
powershell
PS C:\Set-NfsServerConfiguration -EnableNFSV2 $false -EnableNFSV3 $false
Although most of the LDAP vulnerabilities affected all versions of Windows, with CVE-2022-29131 an authenticated attacker could exploit the vulnerability over the network on a domain controller running Windows Server 2019, Windows 10, Windows 11 (x64/arm64), or Windows Server 2022.
CVE-2022-22012 and CVE-2022-29130 were listed as important remote code execution (RCE) vulnerabilities that also affected domain controllers, specifically LDAP. Although, according to the CVSS score for both vulnerabilities, they were deemed critical. An unauthenticated attacker could send a specially crafted request to a vulnerable server that would allow the attacker to remotely execute code within the SYSTEM account context. According to Microsoft, this vulnerability could only be exploited if the MaxReceiveBuffer LDAP policy was set to a value higher than the default value (10,485,760); otherwise, the system was not vulnerable.
CVE-2022-29139 was also listed as important and it differed from the other LDAP vulnerabilities in that it flipped the RCE on its head. If an LDAP client connected to a malicious LDAP server from a Windows host, the malicious server could allow an attacker to remotely execute code within the LDAP client.
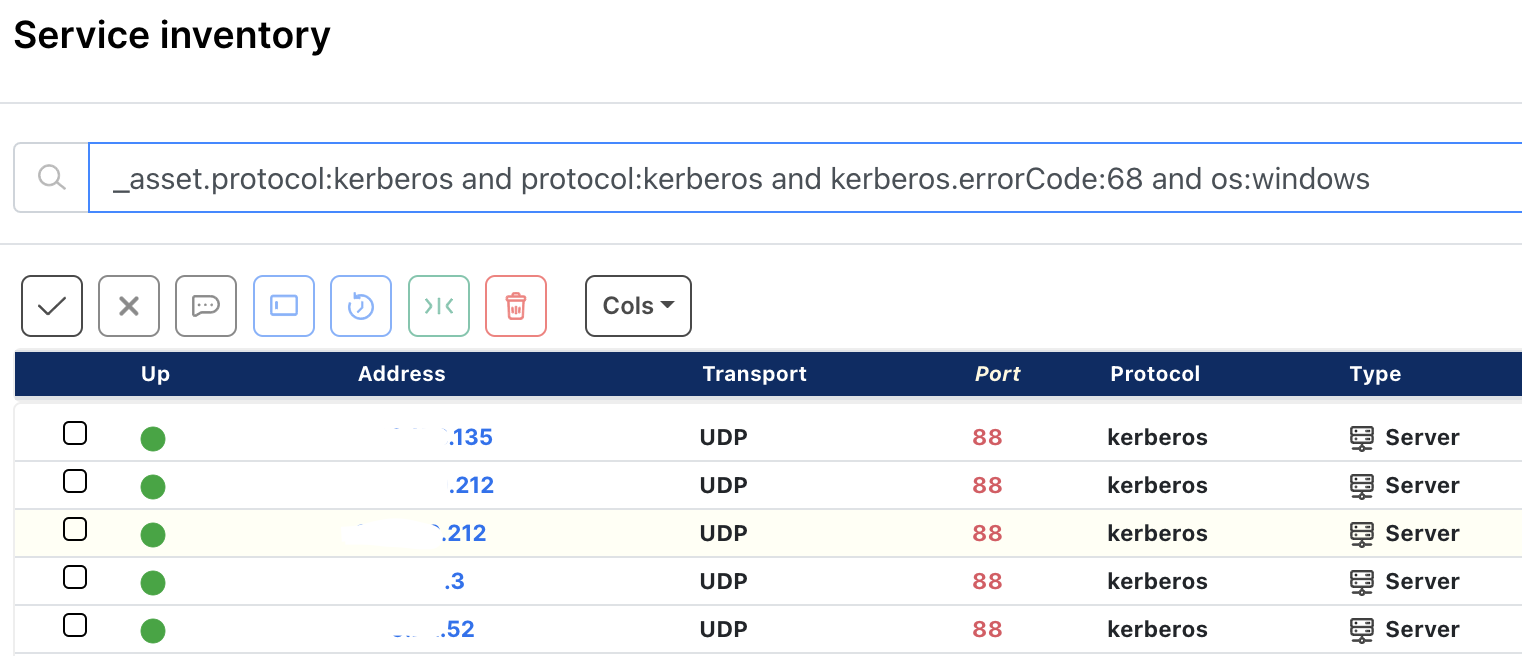
How runZero users found potentially vulnerable Windows Kerberos assets #
From the Service Inventory page, runZero users used the following query to locate Windows NFS assets within their network:
_asset.protocol:kerberos and protocol:kerberos and kerberos.errorCode:68 and os:windows
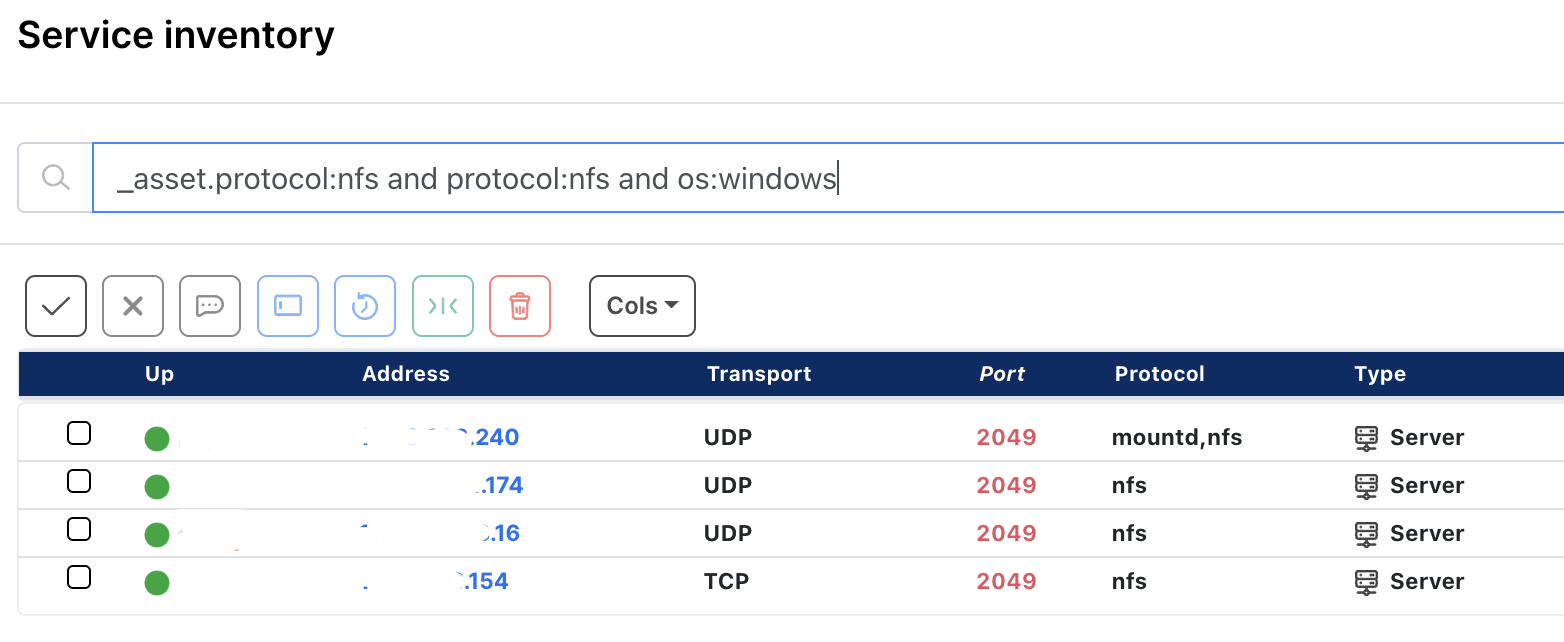
How runZero users found potentially vulnerable Windows NFS assets #
From the Service Inventory page, runZero users used the following query to locate Windows NFS assets within their network:
_asset.protocol:nfs and protocol:nfs and os:windows
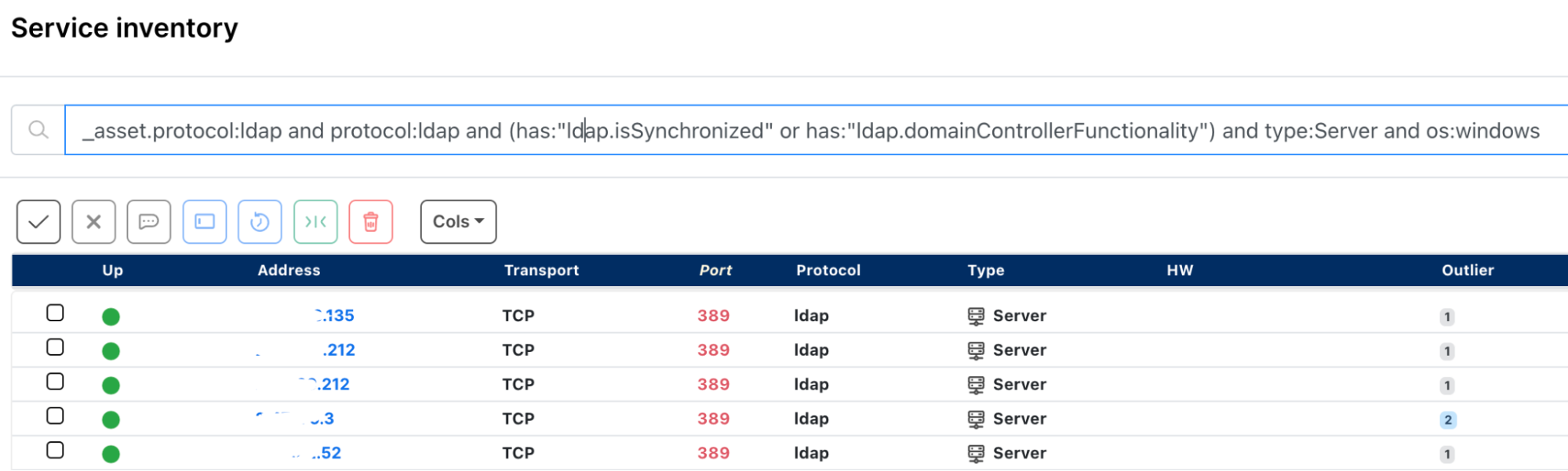
How runZero users found potentially vulnerable Windows domain controller instances #
From the Service Inventory page, runZero users used the following query to locate Windows domain controller assets running LDAP within their network:
_asset.protocol:ldap and protocol:ldap and (has:"ldap.isSynchronized" or has:"ldap.domainControllerFunctionality") and type:server and os:windows
As always, any prebuilt queries we create are available from our Queries Library. Check out the library for other useful inventory queries.