Latest Fortinet vulnerabilities: CVE-2025-59718 and CVE-2025-59719 #
Fortinet has issued an advisory describing authentication bypass vulnerabilities in multiple Fortinet products, including FortiWeb, FortiProxy, FortiSwitchManager, and other products running FortiOS. Successful exploitation of these vulnerabilities could allow a remote, unauthenticated adversary to bypass authentication on systems when they are configured to use Single Sign-On via FortiCloud. These vulnerabilities, designated CVE-2025-59718 and CVE-2025-59719, are rated critical with a base CVSS score of 9.1.
Note that there is evidence that this vulnerability is being actively exploited in the wild and was added to the CISA KEV list on December 16th, 2025.
The following versions are affected:
- FortiOS 7.6 versions 7.6.0 through 7.6.3
- FortiOS 7.4 versions 7.4.0 through 7.4.8
- FortiOS 7.2 versions 7.2.0 through 7.2.11
- FortiOS 7.0 versions 7.0.0 through 7.0.17
- FortiProxy 7.6 versions 7.6.0 through 7.6.3
- FortiProxy 7.4 versions 7.4.0 through 7.4.10
- FortiProxy 7.2 versions 7.2.0 through 7.2.14
- FortiProxy 7.0 versions 7.0.0 through 7.0.21
- FortiSwitchManager 7.2 versions 7.2.0 through 7.2.6
- FortiSwitchManager 7.0 versions 7.0.0 through 7.0.5
- FortiWeb 8.0 version 8.0.0
- FortiWeb 7.6 versions 7.6.0 through 7.6.4
- FortiWeb 7.4 versions 7.4.0 through 7.4.9
What are Fortinet FortiWeb, FortiProxy, FortiSwitchManager, and FortiOS? #
Fortinet FortiWeb is a specialized Web Application Firewall (WAF) that protects web applications and APIs from known and unknown threats by inspecting HTTP traffic and enforcing security policies to block attacks.
Fortinet FortiProxy is a high-performance secure web gateway platform.
Fortinet FortiSwitchManager is a software suite for managing fleets of Fortinet devices.
Fortinet FortiOS is a custom operating system common to many Fortinet products.
What is the impact? #
Successful exploitation of the vulnerability would allow a remote unauthenticated adversary to bypass authentication checks for vulnerable systems. This may allow complete compromise of the vulnerable systems.
Are updates or workarounds available? #
Fortinet recommends upgrading affected systems to the new versions:
- FortiOS 7.6 - Upgrade to 7.6.4 or above
- FortiOS 7.4 - Upgrade to 7.4.9 or above
- FortiOS 7.2 - Upgrade to 7.2.12 or above
- FortiOS 7.0 - Upgrade to 7.0.18 or above
- FortiProxy 7.6 - Upgrade to 7.6.4 or above
- FortiProxy 7.4 - Upgrade to 7.4.11 or above
- FortiProxy 7.2 - Upgrade to 7.2.15 or above
- FortiProxy 7.0 - Upgrade to 7.0.22 or above
- FortiSwitchManager 7.2 - Upgrade to 7.2.7 or above
- FortiSwitchManager 7.0 - Upgrade to 7.0.6 or above
- FortiWeb 8.0 - 8.0.1 or above
- FortiWeb 7.6 - Upgrade to 7.6.5 or above
- FortiWeb 7.4 - Upgrade to 7.4.10 or above
As a temporary workaround, disabling Single Sign-On via FortiCloud may mitigate this vulnerability.
How to find potentially vulnerable systems with runZero #
From the Asset Inventory, use the following query to locate potentially impacted assets:
product:"Fortinet FortiWeb" OR
(os:="Fortinet FortiOS" AND
os_version:>0 AND
((os_version:>="7.6.0" AND os_version:<="7.6.3") OR
(os_version:>="7.4.0" AND os_version:<="7.4.8") OR
(os_version:>="7.2.0" AND os_version:<="7.2.11") OR
(os_version:>="7.0.0" AND os_version:<="7.0.17")))October 2025: CVE-2025-49201, CVE-2025-49201 #
In October 2025, Fortinet disclosed vulnerabilities in certain versions of their FortiSwitch Manager and FortiPAM and products.
August 2025: CVE-2025-52970 (FortiWeb) #
Fortinet has issued an advisory for a vulnerability affecting certain versions of their FortiWeb product where the software improperly handles session cookie parameters, resulting in an authentication bypass vulnerability. To exploit this flaw, a remote, unauthenticated adversary must possess specific non-public information about the device and a target user. Successful exploitation allows the adversary to send a specially crafted request and log in as any existing user on the device. The vulnerability, designated CVE-2025-52970, is rated high with a base CVSS score of 7.7.
The following versions are affected
- FortiWeb 7.0 versions 7.0.0 through 7.0.10
- FortiWeb 7.2 versions 7.2.0 through 7.2.10
- FortiWeb 7.4 versions 7.4.0 through 7.4.7
- FortiWeb 7.6 versions 7.6.0 through 7.6.3
What is the impact? #
Successful exploitation of the vulnerability would allow a remote unauthenticated adversary to gain administrative access to the system.
Are updates or workarounds available? #
Upgrade affected systems to the new versions
- FortiWeb 7.0 upgrade to version 7.0.11 or later
- FortiWeb 7.2 upgrade to version 7.2.11 or later
- FortiWeb 7.4 upgrade to version 7.4.8 or later
- FortiWeb 7.6 upgrade to version 7.6.4 or later
How to find potentially vulnerable systems with runZero #
From the Software Inventory, use the following query to locate potentially impacted assets:
vendor:=Fortinet AND product:=FortiWebAugust 2025: CVE-2025-25256 (FortiSIEM) #
Fortinet has issued an advisory for a vulnerability affecting certain versions of their FortiSIEM product where the software improperly neutralizes special elements used in an OS command, resulting in an OS command injection vulnerability that allows a remote, unauthenticated adversary to execute unauthorized code or commands via crafted CLI requests. The vulnerability, designated CVE-2025-25256, is rated critical with a base CVSS score of 9.8.
There is evidence that this vulnerability is being actively exploited in the wild.
The following versions are affected
- FortiSIEM 5.4 all versions
- FortiSIEM 6.1 all versions
- FortiSIEM 6.2 all versions
- FortiSIEM 6.3 all versions
- FortiSIEM 6.4 all versions
- FortiSIEM 6.5 all versions
- FortiSIEM 6.6 all versions
- FortiSIEM 6.7 versions 6.7.0 through 6.7.9
- FortiSIEM 7.0 versions 7.0.0 through 7.0.3
- FortiSIEM 7.1 versions 7.1.0 through 7.1.7
- FortiSIEM 7.2 versions 7.2.0 through 7.2.5
- FortiSIEM 7.3 versions 7.3.0 through 7.3.1
What is the impact? #
Successful exploitation of the vulnerability would allow a remote unauthenticated adversary to execute arbitrary commands on the remote system, potentially including operating system commands with the privileges of the vulnerable process.
Are updates or workarounds available? #
Upgrade affected systems to the new versions
- FortiSIEM 5.4 migrate to a fixed release
- FortiSIEM 6.1 migrate to a fixed release
- FortiSIEM 6.2 migrate to a fixed release
- FortiSIEM 6.3 migrate to a fixed release
- FortiSIEM 6.4 migrate to a fixed release
- FortiSIEM 6.5 migrate to a fixed release
- FortiSIEM 6.6 migrate to a fixed release
- FortiSIEM 6.7 upgrade to version 6.7.10 or later
- FortiSIEM 7.0 upgrade to version 7.0.4 or later
- FortiSIEM 7.1 upgrade to version 7.1.8 or later
- FortiSIEM 7.2 upgrade to version 7.2.6 or later
- FortiSIEM 7.3 upgrade to version 7.3.2 or later
How to find potentially vulnerable systems with runZero #
From the Software Inventory, use the following query to locate potentially impacted assets:
vendor:="Fortinet" product:="FortiSIEM"May 2025: (CVE-2025-32756) #
Fortinet has issued an advisory for a vulnerability affecting their FortiVoice, FortiMail, FortiNDR, FortiRecorder and FortiCamera products. Note that there is evidence that this vulnerability is actively being exploited in the wild.
The vulnerability, designated CVE-2025-32756, is rated critical with a base CVSS score of 9.8. Successfully exploiting this vulnerability would allow a remote, unauthenticated attacker to execute arbitrary code.
What is the impact? #
For affected product versions, a remote unauthenticated attacker may execute arbitrary code or commands. Fortinet has included indicators-of-compromise (IoCs) within the advisory to help determine whether a system has been compromised.
Are updates or workarounds available? #
In addition to disabling, or restricting access to the HTTP/HTTPS administrative interface, Fortinet recommends upgrading the following versions of affected products:
- FortiCamera 2.1.0 through 2.1.3 to be upgraded to 2.1.4 or later
- FortiCamera 1.1 and 2.0 to be migrated to a fixed release
- FortiMail 7.6.0 through 7.6.2 to be upgraded to 7.6.3 or later
- FortiMail 7.4.0 through 7.4.4 to be upgraded to 7.4.5 or later
- FortiMail 7.2.0 through 7.2.7 to be upgraded to 7.2.8 or later
- FortiMail 7.0.0 through 7.0.8 to be upgraded to 7.0.9 or later
- FortiNDR 7.6.0 to be upgraded to 7.6.1 or later
- FortiNDR 7.4.0 through 7.4.7 to be upgraded to 7.4.8 or later
- FortiNDR 7.2.0 through 7.2.4 to be upgraded to 7.2.5 or later
- FortiNDR 7.1 to be migrated to a fixed release
- FortiNDR 7.0.0 through 7.0.6 to be upgraded to 7.0.7 or later
- FortiNDR 1.1 through 1.5 to be migrated to a fixed release
- FortiRecorder 7.2.0 through 7.2.3 to be upgraded to 7.2.4 or later
- FortiRecorder 7.0.0 through 7.0.5 to be upgraded to 7.0.6 or later
- FortiRecorder 6.4.0 through 6.4.5 to be upgraded to 6.4.6 or later
- FortiVoice 7.2.0 to be upgraded to 7.2.1 or above
- FortiVoice 7.0.0 through 7.0.6 to be upgraded to 7.0.7 or later
- FortiVoice 6.4.0 through 6.4.10 to be upgraded to 6.4.11 or later
How to find potentially vulnerable systems with runZero #
From the Asset Inventory, use the following query to locate systems running potentially vulnerable software:
hw:="Fortinet FortiRecorder" OR hw:="Fortinet FortiNDR" OR hw:="Fortinet FortiMail" OR (hw:"Fortinet" AND type:"SIP Gateway")How to find potentially vulnerable FortiCamera systems with runZero #
From the Service Inventory, use the following query to locate systems running potentially vulnerable software:
hw:"Fortinet" AND _asset.protocol:http AND protocol:http AND (((has:http.head.wwwAuthenticate OR has:last.http.head.wwwAuthenticate) AND http.head.wwwAuthenticate:FortiCamera) OR (has:tls.subject AND tls.subject:FortiCamera))
January 2025: (CVE-2024-55591, CVE-2023-37936) #
Fortinet issued an advisory for a vulnerability affecting their FortiOS and FortiProxy products that is actively being exploited in the wild.
- CVE-2024-55591 detailed in FG-IR-24-535 is rated critical with a CVSS score of 9.6 and may allow unauthenticated attacker to gain administrator privileges.
Fortinet also issued an advisory for their FortiSwitch product.
- CVE-2023-37936 detailed in FG-IR-23-260 is rated critical with a CVSS score of 9.6 and may allow unauthenticated attacker to execute arbitrary code.
What is the impact? #
For affected versions of FortiOS and FortiProxy vulnerable to CVE-2024-55591, a remote attacker may gain administrator privileges bypassing authentication. Fortinet included IoCs within the advisory.
Due to the use of a hard-coded cryptographic key in vulnerable versions of the FortiSwitch product, an unauthenticated attacker with the key could remotely perform arbitrary code execution.
Are updates or workarounds available? #
In addition to disabling, or restricting access to the HTTP/HTTP administrative interface, Fortinet recommends upgrading the following versions of affected products:
CVE-2024-55591
- FortiOS 7.0.0 through 7.0.16 to be upgraded to 7.0.17 or later
- FortiProxy 7.2.0 through 7.2.12 to be upgraded to 7.2.13 or later
- FortiProxy 7.0.0 through 7.0.19 to be upgraded to 7.0.20 or later
CVE-2023-37936
- FortiSwitch 7.4.0 to be upgraded to 7.4.1 or later
- FortiSwitch 7.2.0 through 7.2.5 to be upgrade to 7.2.6 or later
- FortiSwitch 7.0.0 through 7.0.7 to be upgraded to 7.0.8 or later
- FortiSwitch 6.4.0 through 6.4.13 to be upgraded to 6.4.14 or later
- FortiSwitch 6.2.0 through 6.2.7 to be upgraded to 6.2.8 or later
- FortiSwicth 6.0.0 through 6.0.7 should be migrated to a fixed release
How to find potentially vulnerable systems with runZero #
From the Asset Inventory, use the following query to locate systems running potentially vulnerable software:
os:"FortiOS" OR hw:"FortiSwitch" OR hw:"FortiProxy"December 2024: (CVE-2023-34990) #
Fortinet issued advisories for their FortiWLM product.
- CVE-2023-34990 detailed in FG-IR-23-144 was rated critical with a CVSS score of 9.6 and may have allowed an unauthenticated attacker to read sensitive files.
What was the impact? #
An unauthenticated attacker may have been able to manipulate paths through the FortiWLM application and perform a path traversal in order to gain access to sensitive files outside the application root directory on the host machine.
Are updates or workarounds available? #
Fortinet recommended upgrading the following versions:
- FortiWLM 8.6.0 through 8.6.5 to be upgraded to 8.6.6 or above
- FortiWLM 8.5.0 through 8.5.4 to be upgrade to 8.5.5 or above
How to find potentially vulnerable systems with runZero #
From the Service Inventory, use the following query to locate systems running potentially vulnerable software:
html.title:FortiWLMOctober 2024: (CVE-2023-50176, CVE-2024-23666) #
Fortinet issued advisories for its FortiAnalyzer, FortiAnalyzer-BigData, FortiManager, and FortiOS products.
- CVE-2023-50176 detailed in FG-IR-23-475 was rated high with a CVSS score of 7.1, and may have allowed an unauthenticated attacker to hijack a user session.
- CVE-2024-23666 detailed in FG-IR-23-396 was rated high with a CVSS score of 7.1 and may have allowed an authenticated, read-only user the ability to execute "sensitive operations".
What was the impact? #
CVE-2024-23666, which affected FortiAnalyzer and FortiManager products, required that an attacker (or malicious user) was authenticated against the system. A read-only user could potentially execute sensitive operations through crafted requests, bypassing client-side enforcement through the web interface. CVE-2023-50176, which affected the SSLVPN component of FortiOS, was a session fixation vulnerability that allowed an unauthenticated attacker the ability to hijack an authenticated user's session via a "phishing SAML authentication link".
Are updates or workarounds available? #
The vendor released patches for all affected products. They recommended following the upgrade path using their upgrade tool.
How to find potentially vulnerable systems with runZero #
From the Asset Inventory, use the following query to locate systems running potentially vulnerable software:
hw:FortiManager OR hw:FortiAnalyzer OR os:FortiOSMarch 2024 #
On March 12th, 2024, Fortinet disclosed several vulnerabilities in their FortiOS, FortiProxy, and FortiClient products:
FG-IR-23-328 – a buffer overflow vulnerability in the handling of form-based authentication in the FortiOS and FortiProxy captive portals, allowing remote, unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code. This vulnerability has been assigned CVEs CVE-2023-42789 and CVE-2023-42790. These vulnerabilities have a CVSS score of 9.3, indicating that they are critical.
FG-IR-24-007 – a SQL injection vulnerability in the FortiClient Enterprise Management Server. This vulnerability has been designated CVE-2023-48788, and has been given a CVSS score of 9.8 (critical).
FG-IR-23-390 – a log injection vulnerability in the FortiClient Enterprise Management Server. This vulnerability has been assigned CVE-2023-47534 and a CVSS score of 7.7 (high).
FG-IR-23-103 – a remote code execution vulnerability in the FortiManager product. This vulnerability has been designated CVE-2023-36554 with a CVSS score of 7.7 (high). Note that the vulnerable subsystem is not installed by default.
FG-IR-23-013 – an information disclosure vulnerability in the FortiGuard SSL-VPN product. This vulnerability has been designated CVE-2024-23112 and given a CVSS score of 7.2 (high).
How to find FortiOS, FortiProxy or FortiClient operating systems #
From the Asset Inventory, use the following query to locate assets running the FortiOS or FortiProxy operating systems, which may be vulnerable:
os:"FortiOS" OR os:"FortiProxy"Additionally, from the Services Inventory, use the following query to locate potentially vulnerable systems:
html.title:="FortiClient Endpoint Management Server"February 2024: (CVE-2024-21762) #
On February 8th, 2024, Fortinet disclosed a serious vulnerability in their FortiOS operating system, used by multiple Fortinet products.
The issue, CVE-2024-21762, allowed attackers to execute arbitrary code on vulnerable devices. The vendor has indicated that this is a critical vulnerability. The vendor reports that there are indications that this vulnerability may be actively exploited in the wild. Upon successful exploitation of these vulnerabilities, attackers could execute arbitrary code on the vulnerable system.
Fortinet released an update to mitigate this issue and all users were urged to update immediately. Additionally, the vendor indicated that disabling the SSL-VPN functionality of the device would mitigate the issue.
How to find FortiOS devices #
From the Asset Inventory, use the following query to locate assets running the FortiOS operating system which may potentially be vulnerable:
os:"FortiOS" AND tcp:443
October 2022: (CVE-2022-40684) #
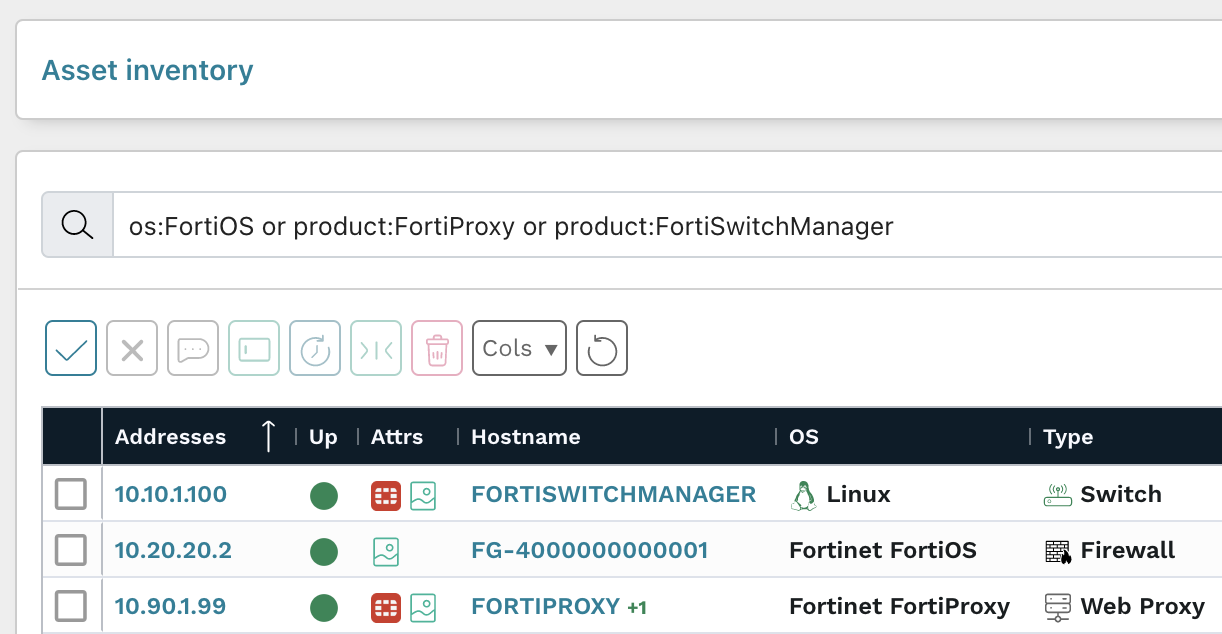
News surfaced in October 2022 of a critical authentication bypass vulnerability present in the web administration interface of some Fortinet products. Successful exploitation of this vulnerability (tracked as CVE-2022-40684) via crafted HTTP and HTTPS requests could provide remote attackers with admin-level command execution on vulnerable FortiOS devices including FortiGate firewalls, FortiProxy web proxies, and FortiSwitchManager assets.
With a CVSS critical score of 9.6, attackers running admin-level commands on compromised assets may have had the ability to persist presence, explore connected internal networks, and exfiltrate data. At the time Fortinet was aware of at least one exploit of this vulnerability in the wild, and Bleeping Computer offered a Shodan search showing more than 140k publicly accessible FortiGate devices potentially running vulnerable FortiOS. Additionally, security researchers with Horizon3.ai planned on publishing an exploit PoC. For admins wanting to check if a FortiOS/FortiProxy/FortiSwitchManager asset had been exploited, Fortinet provides an indicator of compromise (see the “Exploitation Status” section).
Fortinet called out the vulnerable FortiOS, FortiProxy, and FortiSwitchManager versions in their advisory and had made updates available for affected products. Admins were advised to ensure that affected models were updated to the latest version as soon as possible. If updates could not be completed in the near term, Fortinet provided some mitigation steps (see the “Workaround” section) that could be taken to secure vulnerable assets.
How to find FortiOS, FortiProxy, and FortiSwitchManager assets #
From the Asset Inventory, runZero users entered the following pre-built query to locate FortiOS, FortiProxy, and FortiSwitchManager assets:
os:FortiOS or product:FortiProxy or product:FortiSwitchManager